Join Our Groups
TOPIC 3: COMPUTER NETWORKS AND COMMUNICATIONS
Introduction to Local Area Network (LAN) and Wide Area Network (WAN)
The Computer Network
Describe a Computer Network
A network can be defined as a group of computers and other devices connected in some ways so as to be able to exchange data. Each of the devices on the network can be thought of as a node; each node has a unique address. Addresses are numeric quantities that are easy for computers to work with, but not for humans to remember. Example: 204.160.241.98 Some networks also provide names that humans can more easily remember than numbers. Example: www.javasoft.com, corresponding to the above numeric address.
A computer network This is a digital telecommunications network which allows nodes to share resources. In computer networks, networked computing devices exchange data with each other using a data link. The connections between nodes are established using either cable media or wireless media.
The Local area Network (LAN)
Explain Local area Network (LAN)
LOCAL AREA NETWORK (LAN)
- Local Area Network is privately owned communications network that spans a small geographic area, such as single building or buildings close to each other. May be school or college campus Examples: Ethernet, Local Talk, Token Ring, FDDI, ATMIn addition to operating in a limited space in limited space, LANs are also typically owned, controlled and manage by a single person or organization. Most of the LANs are built with relatively inexpensive hardware such as Ethernet cables, network adapters, and hubs
WIDE AREA NETWORK (WAN)
- Wide Area Network is a computer network that can span a very large geographic area, e.g., multiple cities, countries, continents or even across the word. Examples: ARPANET, X.25, Frame Relay, SMDS, ATM Internet is the largest WAN, spanning the earth. WAN is the geographically dispersed collection of LANs. A communication devices called router can connect LANs in to WAN. WAN differ from LAN in several ways. Most of the WANs are not owned by any organization but rather exist under collective or distributed ownership and management.
The table below shows the difference between LAN and WAN.
| FEATURE | LAN | WAN |
| Scale of sharing | Less and limited | Far greater and worldwide |
| Communication media | Uses cable such as coaxial and UTP | Satellite, microwaves or telecommunication links |
| Installation cost | Low | High |
| Network coverage | Small area, over a single building or college campus | Cities, state and countries |
The Accessories Used for Computer Network Connections
List of Accessories Used for Computer Network Connections
Computer network components include the major parts that are needed to install a network both at the office and home level. Before delving into the installation process, you should be familiar with each part so that you could choose and buy the right component that fits with your network system.
These hardware components include cable, Hub, Switch, NIC (network interface card), modem and router. Depending on the type of network you are going to install, some of the parts can be eliminated. For example, in a wireless network you don’t need cables, hubs so on.
Computer network requires the following devices (some of them are optional):-
- Network Interface Card (NIC)
- Hub Switches
- Cables and connectors
- Router Modem
NETWORK INTERFACE CARD (NIC)
- This is a device that enables a computer to talk with other computer/network. Using unique hardware addresses (MAC address)encoded on the card chip, the data-link protocol employs these addresses to discover other systems on the network so that it can transfer data to the right destination.
There aretwo types of network cards:
- Wired
- Wireless
The wired NIC uses cables and connectors as a medium to transfer data, whereas in the wireless card, the connection is made using antenna that employs radio wave technology. All modern laptop computers incorporated wireless NIC in addition to the wired adapter.

HUB
- Hub is a device that splits a network connection into multiple computers. It is like a distribution center. When a computer request information from a network or a specific computer, it sends the request to the hub through a cable. The hub will receive the request and transmit it to the entire network. Each computer in the network should then figure out whether the broadcast data is for them or not. Currently Hubs are becoming obsolete and replaced by more advanced communication devices such asSwitches and Routers.

SWITCH
- This is a telecommunication device grouped as one of computer network components. Switch is like a Hub but built in with advanced features. It uses physical device addresses in each incoming messages so that it can deliver the message to the right destination or port.Like Hub, switch don’t broadcast the received message to entire network, rather before sending it checks to which system or port should the message be sent. In other words switch connects the source and destination directly which increases the speed of the network. Both switch and hub have common features: Multiple RJ-45 ports, power supply and connection lights.
CABLES AND CONNECTORS
- Cable is one way of transmission media which can transmit communication signals. The wired network typology uses special type of cable to connect computers on a network.There are a number of solid transmission Media types, which are listed below.
Twisted pair wire It is classified as Category 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 5E, 6 and 7. Category 5E, 6 and 7 are high-speed cables that can transmit 1Gbps or more.
Coaxial cable Coaxial cable more resembles like TV installation cable. It is more expensive than twisted-pair cable but provide high data transmission speed.
Fiber-optic cable It is a high-speed cable which transmits data using light beams through a glass bound fibers. Fiber-optic cable is high data transmission cable comparing to the other cable types. But the cost of fiber optics is very expensive which can only be purchased and installed on governmental level.
ROUTER
When we talk about computer network components, the other device that used to connect a LAN with an internet connection is called Router.
When you have two distinct networks (LANs) or want to share a single internet connection to multiple computers, we use a Router.In most cases, recent routers also include a switch which in other words can be used as a switch. You don’t need to buy both switch and router, particularly if you are installing small business and home networks.
There are two types of Router: wired and wireless. The choice depends on your physical office/home setting, speed and cost.
MODEMS
A modem enables you to connect your computer to the available internet connection over the existing telephone line. Like NIC, Modem is not integrated with a computer motherboard. It comes as separate part which can be installed on the PCI slots found on motherboard.A modem is not necessary for LAN, but required for internet connection such as dial-up and DSL.There are some types of modems, which differs in speed and transmission rate.
Standard PC modem or Dial-up modems (56Kb data transmission speed), Cellular modem (used in a laptop that enables to connect while on the go),cable modem (500 times faster than standard modem)and DSL Modems are the most popular.
The Importance of Computer Networks
Explain the Importance of Computer Networks
ADVANTAGES OF COMPUTER NETWORKS
A network is two or more computers connected together to share information and files between them. Businesses aren't the only ones that can benefit from creating a network. Home users can enjoy sharing music, movies and printers from any computer. Computer network provides several advantages which include but not limited to the following:
- It enhances communication and availability of information. Networking, especially with full access to the web, allows ways of communication that would simply be impossible before it was developed. Instant messaging can now allow users to talk in real time and send files to other people wherever they are in the world, which is a huge boon for businesses. Also, it allows access to a vast amount of useful information, including traditional reference materials and timely facts, such as news and current events.
- It allows for more convenient resource sharing. This benefit is very important, particularly for larger companies that really need to produce huge numbers of resources to be shared to all the people. Since the technology involves computer-based work, it is assured that the resources they wanted to get across would be completely shared by connecting to a computer network which their audience is also using.
- It makes file sharing easier. Computer networking allows easier accessibility for people to share their files, which greatly helps them with saving more time and effort, since they could do file sharing more accordingly and effectively.
- It is highly flexible. This technology is known to be very flexible, as it gives users the opportunity to explore everything about essential things, such as software without affecting their functionality. Plus, people will have the accessibility to all information they need to get and share.
- It is an inexpensive system. Installing networking software on your device would not cost too much, as you are assured that it lasts and can effectively share information to your peers. Also, there is no need to change the software regularly, as mostly it is not required to do so.
- It increases cost efficiency. With computer networking, you can use a lot of software products available on the market which can just be stored or installed in your system or server, and can then be used by various workstations.
- It boosts storage capacity. Since you are going to share information, files and resources to other people, you have to ensure all data and content are properly stored in the system. With this networking technology, you can do all of this without any hassle, while having all the space you need for storage
Despite of the aforementioned benefits, computer networks are likely to have the following disadvantages.
- It lacks independence. Computer networking involves a process that is operated using computers, so people will be relying more of computer work, instead of exerting an effort for their tasks at hand. Aside from this, they will be dependent on the main file server, which means that, if it breaks down, the system would become useless, making users idle.
- It poses security difficulties. Because there would be a huge number of people who would be using a computer network to get and share some of their files and resources, a certain user’s security would be always at risk. There might even be illegal activities that would occur, which you need to be careful about and aware of.
- It lacks robustness. As previously stated, if a computer network’s main server breaks down, the entire system would become useless. Also, if it has a bridging device or a central linking server that fails, the entire network would also come to a standstill. To deal with these problems, huge networks should have a powerful computer to serve as file server to make setting up and maintaining the network easier.
- It allows for more presence of computer viruses and malware. There would be instances that stored files are corrupt due to computer viruses. Thus, network administrators should conduct regular check-ups on the system, and the stored files at the same time.
- Its light policing usage promotes negative acts. It has been observed that providing users with internet connectivity has fostered undesirable behavior among them. Considering that the web is a minefield of distractions—online games, humor sites and even porn sites—workers could be tempted during their work hours. The huge network of machines could also encourage them to engage in illicit practices, such as instant messaging and file sharing, instead of working on work-related matters. While many organizations draw up certain policies on this, they have proven difficult to enforce and even engendered resentment from employees.
- It requires an efficient handler. For a computer network to work efficiently and optimally, it requires high technical skills and know-how of its operations and administration. A person just having basic skills cannot do this job. Take note that the responsibility to handle such a system is high, as allotting permissions and passwords can be daunting. Similarly, network configuration and connection is very tedious and cannot be done by an average technician who does not have advanced knowledge.
- It requires an expensive set-up. Though computer networks are said to be an inexpensive system when it is already running, its initial set up cost can still be high depending on the number of computers to be connected. Expensive devices, such as routers, switches, hubs, etc., can add up to the cost. Aside from these, it would also need network interface cards (NICs) for workstations in case they are not built in.
Network Physical Topologies
The Different Network Topologies
Identify Different Network Topologies
The term “Topology” refers to the way in which the end points or stations/computer systems, attached to the networks, are interconnected.
Network topology defines the way in which computers, printers and other devices are connected or Network topology is the arrangement of the various elements (links, nodes, etc.) of a communication network.
The topology you choose to implement will influence many factors in the way your network works. When we refer to a network topology, we may be referring to its physical or its logical topology.
Physical topology refers to the way in which a network is laid out physically, the actual layout of the wire or media, two or more devices connect to a link, and two or more links form a topology.
Logical topology defines how the hosts access the media to send data. Shows the flow of data on a network.
Logical Topology
- The logical topology of a network determines how the hosts communicate across the medium. The two most common types of logical topologies are broadcast and token passing.The use of a broadcast topology indicates that each host sends its data to all other hosts on the network medium. There is no order that the stations must follow to use the network. It is first come, first serve. Ethernet works this way as will be explained later in the course.The second logical topology is token passing.
- In this type of topology, an electronic token is passed sequentially to each host. When a host receives the token, that host can send data on the network. If the host has no data to send, it passes the token to the next host and the process repeats itself. Two examples of networks that use token passing are Token Ring and Fiber Distributed Data Interface (FDDI). A variation of Token Ring and FDDI is Arcnet. Arcnet is token passing on a bus topology.
The Network Physical Topologies
Explain Network Physical Topologies
TYPES OF PHYSICAL TOPOLOGIES
Physical topologies are defined purely by the way in which the networking media connects the devices. A diagram of the physical topology of a network shows the physical path of the media take to reach each of the devices on the network. Depending on the requirements, there are different topologies to construct a network.
- Mesh topology
- Star topology
- Tree topology
- Bus topology
- Ring topology
- Cellular topology
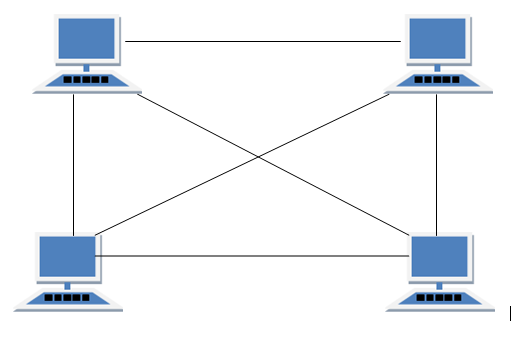
1. Mesh topology
- In a mesh topology, every device has a dedicated point-to-point link to every other device. The term dedicated means that the link carries traffic only between the two devices it connects. To connect n nodes in Mesh topology, we require n (n-1)/2 duplex mode links.
One practical example of a mesh topology is the connection of telephone regional offices in which each regional office needs to be connected to every other regional office.
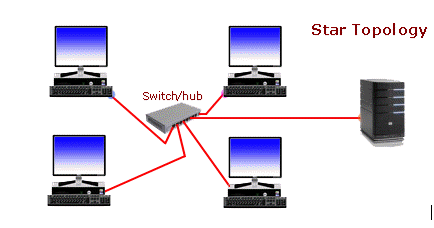
2. Star topology
- In a star topology, each device has a dedicated point-to-point link only to a central controller, usually called a hub. The devices are not directly linked to one another. Unlike a mesh topology, a star topology does not allow direct traffic between devices. The controller acts as an exchange: If one device wants to send data to another, it sends the data to the controller, which then relays the data to the other connected device.
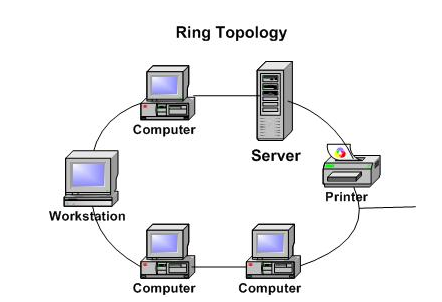
3.Ring topology
- In a ring topology, each device has a dedicated point-to-point connection with only the two devices on either side of it. A signal is passed along the ring in one direction, from device to device, until it reaches its destination.Each device in the ring incorporates a repeater. When a device receives a signal intended for another device, its repeater regenerates the bits and passes them along. A ring is relatively easy to install and reconfigure. Each device is linked to only its immediate neighbours (either physically or logically). To add or delete a device requires changing only two connections. The only constraints are media and traffic considerations (maximum ring length and number of devices). In addition, fault isolation is simplified. Generally in a ring, a signal is circulating at all times. If one device does not receive a signal within a specified period, it can issue an alarm. The alarm alerts the network operator to the problem and its location.However, unidirectional traffic can be a disadvantage. In a simple ring, a break in the ring (such as a disabled station) can disable the entire network. This weakness can be solved by using a dual ring or a switch capable of closing off the break.However, unidirectional traffic can be a disadvantage. In a simple ring, a break in the ring (such as a disabled station) can disable the entire network. This weakness can be solved by using a dual ring or a switch capable of closing off the break.
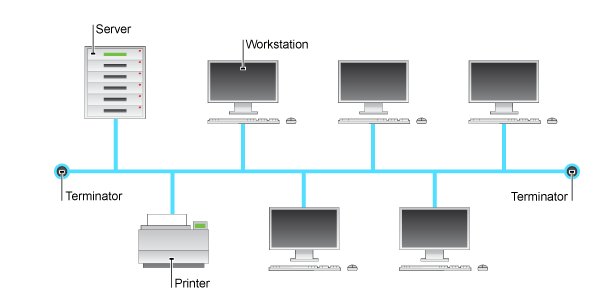
4.Bus topology
A networking topology that connects networking components along a single cable or that uses a series of cable segments that are connected linearly. A network that uses a bus topology is referred to as a “bus network.” Bus networks were the original form of Ethernet networks, using the 10Base5 cabling standard. Bus topology is used for:
- Small work-group local area networks (LANs) whose computers are connected using a thin net cable
- Trunk cables connecting hubs or switches of departmental LANs to form a larger LAN
- Back boning, by joining switches and routers to form campus-wide networks
5. Tree topology
- Tree Topology integrates the characteristics of Star andBus Topology. Earlier we saw how in Physical Star network Topology, computers (nodes) are connected by each other through central hub. And we also saw in Bus Topology, work station devices are connected by the common cable called Bus. After understanding these two network configurations, we can understand tree topology better. In Tree Topology, the number of Star networks are connected using Bus. This main cable seems like a main stem of a tree, and other star networks as the branches. It is also called Expanded Star Topology. Ethernet protocol is commonly used in this type of topology.
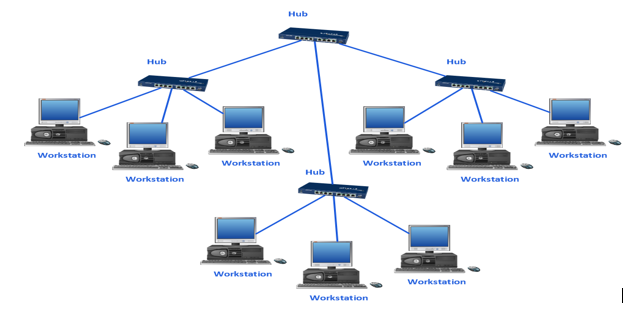
6.Cellular topology
- The cellular topology is applicable only in case of wireless media that does not require cable connection. In wireless media, each point transmits in a certain geographical area called a cell. Each cell represents a portion of the total network area. Devices that are in the cell communicate through a central hub. Hubs in different cells are interconnected. They route data across the network and provide a complete network infrastructure. The data is transmitted in the cellular digital packet data (CDPD) format.
The Advantages and Disadvantage of each Topology
State Advantages and Disadvantages of each Topologies
Advantages of mesh topology
- The use of dedicated links guarantees that each connection can carry its own data load, thus eliminating the traffic problems that can occur when links must be shared by multiple devices.
- Robust, if one link becomes unusable, it does not incapacitate the entire system.
- Advantage of privacy or security.
- Point-to-point links make fault identification and fault isolation easy, Traffic can be routed to avoid links with suspected problems.
Disadvantages of mesh topology
- Required high amount of cabling and the number of I/O ports.
- The sheer bulk of the wiring can be greater than the available space (in walls, ceilings, or floors) can accommodate.
- The hardware required to connect each link (I/O ports and cable) can be prohibitively expensive.
Advantages of star topology
- Less Expensive than mesh topology.
- In a star topology, each device needs only one link and one I/O port to connect it to any number of other devices. This factor also makes it easy to install and reconfigure.
- Less Cabling, Addition and Deletion involves only one connection between the devices and the Hub or Switch.
- Easy for Fault identification and fault isolation. If one link fails, only that link is affected.
Disadvantages of star topology
- One big disadvantage of a star topology is the dependency of the whole topology on one single point, the hub. If the hub goes down, the whole system is dead.
Advantages of ring topology
- Performs better than a bus topology under heavy network load
- Does not require network server to manage the connectivity between the computers
- Very orderly network where every device has access to the token and the opportunity to transmit
Disadvantages of ring topology
- One malfunctioning workstation or bad port in the MAU can create problems for the entire network
- Moves, adds and changes of devices can affect the network
- Network adapter cards and MAU's a Multistation Access Unit are much more expensive than Ethernet cards and hubs
- Much slower than an Ethernet network under normal load
Advantages of bus topology
- Easy to install
- Costs are usually low
- Easy to add systems to network
- Great for small networks
Disadvantages of bus topology
- Out of date technology.
- include difficult reconnection and fault isolation
- Can be difficult to troubleshoot.
- Unmanageable in a large network
- If cable breaks, whole network is down
Advantages of Tree Topology
- It is an extension of Star and bus Topologies, so in networks where these topologies can't be implemented individually for reasons related to scalability, tree topology is the best alternative.
- Expansion of Network is possible and easy.
- Here, we divide the whole network into segments (star networks), which can be easily managed and maintained.
- Error detection and correction is easy.
- Each segment is provided with dedicated point-to-point wiring to the central hub.
- If one segment is damaged, other segments are not affected.
Disadvantages of Tree Topology
- Because of its basic structure, tree topology, relies heavily on the main bus cable, if it breaks whole network is crippled.
- As more and more nodes and segments are added, the maintenance becomes difficult.
- Scalability of the network depends on the type of cable used.
Advantages of cellular topology
- Troubleshooting is easy
- Hub to hub fault tracking is more complicated, but allows simple fault isolation.
Disadvantages of cellular topology
- When the central hub fails, all the unit in the assigned range of cell are affected.






EmoticonEmoticon