Join Our Groups
TOPIC 2
THE
SOLAR SYSTEM
Solar System is the arrangement of sun, planets and
other solid objects in the space in relation to the position of the sun. The planets are not arranged in a single
line from the sun, they are scattered in the space.
Components of the Solar System
The
solar system is made up of the sun, planets, moons, natural satellites,
asteroids, meteors, comets, dust, ice, and interplanetary space (it contains
interplanetary dust and interplanetary gas). All planets and other bodies
revolve around the sun. The sun is the central body of the solar system, and it
is the only body that generates its own heat. Bodies that revolve around the
sun are kept in their orbits (paths) by the sun’s powerful force of gravity.
There
are eight known planets in the solar system. The planets, starting from the one
closest to the sun are: Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus,
and Neptune.
The
four innermost planets in the solar system, Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars are
also called terrestrial planets. They are called terrestrial because they have
a compact, rocky surface like the Earth's.
Jupiter,
Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune are known as the Jovian (Jupiter-like) planets,
because they are all gigantic compared with Earth, and they have a gaseous
nature like Jupiter's. The Jovian planets are also referred to as the gas
giants, although some or all of them might have small solid cores.
 |
| Solar System |
Importance of the
Components of Solar System
Though
the solar system has many components, the two most important components of the
solar system are the Earth and the sun. The Earth sustains lives of a diversity
of living organisms (plants and animals). The Earth contains numerous resources
that enable living organisms to thrive in it. The Earth’s atmosphere contains
water and air (a mixture of several gases that are used by living organisms for
survival). In general, the Earth is the only planet known to sustain life.
1. Mercury
= 57600,000km
2. Venus
= 107,200,000 km
3. Earth
= 148,800,000km
4. Mars
= 227.200,000km
5. Jupiter
= 772,800,000 km
6. Saturn
= 1,417,600,000km
7. Uranus
= 2,854,400,000 km
8. Neptune
= 4,468,800,000 km
A. SUN
Sun is
the star. It is one among the millions of stars that one sees at night except
that it looks much bigger because it is closer to the earth than other distant
stars. The sun is much larger than other distant stars from the earth. In fact
much larger than all the planets put together. Its diameter is approximately 14
million kilometers and its mass is approximately 330,000 times greater than
that of the earth. The elements that form the material of the sun are also in
different proportion from those of the earth: The sun is composed of
approximately;
·
75%
hydrogen
·
23% helium
·
3% of other elements
The
earth is relatively cold body but the sun is so hot that nearly all molecules
are broken into their separate atoms and all are mixed together into a single
hot gas. Its average surface temperature is about 6000°c, it is much hotter in
the interior where it is about 14,000,000°c.
The sun is the source of all energy that supports life on Earth. The sun is responsible for water cycle and it is responsible for weather conditions and climate. The moon lights the Earth on some days of the month, though it gets its light from the sun.
The sun is the source of all energy that supports life on Earth. The sun is responsible for water cycle and it is responsible for weather conditions and climate. The moon lights the Earth on some days of the month, though it gets its light from the sun.
The Importance of the Sun
1. The sun is very important in the plants’
growth. The sun helps the plants to make their own food by the photosynthesis
process.
2. The sun is very necessary for the
other living organisms, that is, it provides us with light for the vision and
to do our work.
3. The sun provides us with the heat to
warm our bodies.
4. The sun provides some animals and
humans (that feed on plants) with food as it helps the plants to make its own
food by the photosynthesis process.
5. The sun is used in heating water and
warming houses by the solar heater which changes the solar energy of the sun
into the heat energy. The heat energy is used in warming houses and heating
water.
6. The sun is very important in the
formation of the clouds, rain, and winds. The sun evaporates the water in the
seas, lakes and oceans into water vapour. When the water vapour rises in the
sky, it cools and condenses forming the clouds, which eventually forms rain.
B. SOLAR ENERGY
The sun is the source
of all energy in the earth. This is called solar energy. Solar energy is the energy produced by the sun
Uses
of Solar Energy
1. In drying clothes, grains, fruits
and meat.
2. Growing plants: - when plants grow they use energy from the sun to manufacture their
food through the process known as
photosynthesis
3. Solar energy captured in solar panels and stored in batteries provides electricity used
in generating industrial and home appliances like television,
refrigerator, Oven, electric iron
and cooker.
4. Many
everyday items such
as calculators and other low power consuming devices can be powered by solar energy effectively
5. Is
used as a source of vitamin D for human being
6. It
is used for evaporation of water from water bodies which is necessary for rain formation
Coal
energy is the solar energy
stored in the bodies of plants grew thousands of years ago which after being barred under the earth for a very long time turned into coal similarly gas and oil formed from died bodies of organic matters which lived thousands of years ago.
How the use of solar energy promotes
environmental conservation
1. Solar
energy is used by plant during manufacturing its food through the
photosynthesis. In this process plants take up carbon dioxide from the
atmosphere and releasing oxygen. In dome so carbon dioxide is removed from the
atmosphere making the ozone layer safe and more oxygen to be used in
troposphere by other living organisms.
2. Moreover,
Solar energy is clean and safe type of energy suitable for heating and lighting
this is due to the fact that it does not release soot.
3. The
use of solar energy in household’s helps to promote and conceive environment in
the sense that it would reduce the need for firewood and charcoal, where by
both once extracted pollute and destroy forest.
4. The
use of solar energy also reduces the use of fuel like kerosene as a result it
helps to reduce environmental pollution caused by smoke from burning fuel.
5. Formation
of coal and oil:
Coal is solar energy stored in the bodies of plants that grew thousands of
years ago, and which after being buried under the Earth for a very long period,
turned into coal. Similarly, oil was formed from dead bodies of organisms.
6. Formation
of rainfall:
Evaporation of water which is necessary for cloud and finally rainfall
formation also uses solar energy.
Solar energy in relation to the emancipation of women
(how solar energy contribute to the emancipation of women)
1. Helps to reduce the time would
be consumed used by the women searching firewood from forest.
2. The use of solar energy
equipments on cooking makes them to have more time to be involved in money
making activities such as business or farming.
3. Through the use of solar
energy equipments in cooking and other domestic’s tasks, young girls get time
to go to school and private study as it was to the boys.
C. PLANETS
The planets are bodies
that revolve around the sun. Planets revolve around the sun in
anticlockwise direction following paths called orbits.
As they revolve around the sun, they appear to move among the stars. This is
the reason why the Greeks called them the planets, which in their
language means “wandering stars”.
All the light and
the heat of the planets come from the sun. Hence, the temperatures on the
planets depend on their relative distances from the sun. All planets revolve
around the sun in the same direction in orbits that are elliptical and nearly
in the same plane.
They
include:
1. Mercury
2. Venus
3. Earth
4. Mars
5. Jupiter
6. Saturn
7. Uranus
8. Neptune
As
they revolve around the sun they appear to move around the star. That is why
the Greeks called them planets
means “Wandering stars”. All planets
revolve around the sun in the same orbit that are elliptical and nearly the
same plane.
The
time taken to complete an orbit round the sun depends on the distance of the
planet from the sun. All the light and heat of the planets come from the sun.
Hence the temperatures on the planet depend on their relative distances from
the sun. However, Pluto is not a planet
because an object to be a planet, it needs to meet these requirements
(criteria) defined by the International Astronomical Union (IAU) as follows:
i)
It needs to be in orbit around
the sun
ii)
It needs to have enough to
pull itself in a spherical shape
iii)
It needs to have “Cleared
neighborhood of its orbit”
Note: Any
object that doesn’t meet these 3 criteria is considered a dwarf planet. And so, Pluto is a dwarf
planet is not a planet.
PLANETS
POSITION AND CHARACTERISTICS
D. COMETS
Sometimes
at night one sees objects with leading heads and right
tail at the sky. These are
called comets. At present
many scientists believe that comets are
composed of ice crystals and fragment matters. Comets revolve around the sun far beyond the limits of
Pluto. They can be seen from the earth only when they come close to the sun.
 |
| Comet |
E. ASTEROIDS
Asteroids
are solid heavenly bodies revolving around the sun mostly between
the orbits of Mars and Jupiter There are thousands of these, the largest having diameter of less than 800km. These bodies cannot be
seen without a telescope because they are very far away.
Asteroid
|
F. METEORS
Meteors
are process of hard matter falling from
outer space become visible between
110 and 145 km above the earth’s
surface, where as a result of friction with
the atmosphere become hot and usually
disintegrate. When they do completely
disintegrate as they pass through the
atmosphere reach the earth’s surface and are known as meteorites.
 |
| Meteor and Meteorite |
Meteorites are usually made of nickel, iron or silica fragments of disintegrated comets. There are two known meteorites in Tanzania one is found in Mbozi District and the other fell at Malampaka in Kwimba District in 1930. Sometimes meteors reach the earth’s surface with such force, hence they make large holes or craters. An example of such craters in the world is the great meteor crater in Arizona desert in United States of America which is 150 meters deep and about 1 kilometer width.
G. SATELLITES
Satellites are moons of the planets. The number of satellites depends on the nature and size of planet
up to the moment space researches has proved that only seven planets have satellites.
H. THE EARTH
The Earth is the
third planet from the sun. It is the only planet known to have an atmosphere
containing free oxygen, oceans of liquid water on its surface, and supports
life. Earth is the fifth largest of the planets in the solar system, smaller
than the four gas giants namely Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune, but larger
than the three other rocky planets, Mercury, Mars and Venus. We
live on the planet earth. The Earth
is made of the;
·
Atmosphere (air)
·
Hydrosphere (water bodies)
·
The crust solid
·
Molten material
·
Biosphere (living things)
About 3/4
of the earth’s surface is covered by water. In fact no other planet in the
solar system is known to have water bodies, the shape of the earth is a
flattened sphere This flattening is very slight as indicated by measurements in
diameters through poles and at the equator. The diameter through the poles is
12,713 km while at the equator it is 12,757 km.
The Shape of the Earth and
its Evidence
The
Earth is not perfectly round. Its shape is an oblate
spheroid which is a flattened sphere. The flattening is very slight
at the poles than at the equator. There are some several
evidences, which are used to prove that the earth is sphere like structure,
some of them are shown in the following:
(i) SUNRISE AND
SUNSET
The
sunrise and sunset at different places of the earth, people in the east see the
sun earlier than the people in the west due to earth’s rotation from west to
east. If the earth was flat the whole world would have sunrise and sunset at
the same time.
 |
| Spherical earth and Flat
earth |
(ii)
CIRCUMNAVIGATION OF THE EARTH
If
traveling from a certain point of the earth and you go straight around the
earth you will come to the point of origin. The first traveler around the world
named Magellan in 1519 - 1522 proved this; image did not encounter abrupt edge
over the world in his voyage.
 |
| Circumnavigation of the Earth |
(iii)
AERIAL PHOTOGRAPHS
Photographs
taken by satellites or aeroplane from the air show that the earth has a curved
or round shape
 |
| Aerial Photographs |
(iv)
SHIP’S VISIBILITY
If you
are in the coast viewing a ship which is very far you will see the soot, then the pipe and eventually the whole ship
gradually appears. If the earth were flat the ship would have been seen all at once
 |
| Spherical Earth and Flat Earth |
(v) LUNAR ECLIPSE
The
shadow of the earth thrown to the moon during lunar eclipse is always round.
Only a spherical object can give a circular shadow.
THE MOON
The
moon is a natural satellite of the earth It has a solid spherical body with a
diameter of 3456 kilometers. The distance from the earth to the moon is a
384,403 kilometers. The moon takes 129 ½ days to make a complete revolution
around the earth.
The
moon appears to rise in the east and set in the west because the earth spins
from west to
east. Among all planets only the
earth sustains life due to its position from the sun. It is not very close or
very far from the sun. Other body such as Pluto which is very far from the sun
does not sustain life because it is very cold. Likewise Mercury which is very close
to the sun does not sustain life because it is very hot.
EARTH’S MOVEMENT
The earth is in motion all the time. One does not feel this motion because one moves with it, like all other planets, the earth has two motions known as: -
(a) Rotation
(b) Revolution
ROTATION
Rotation refers to the spinning of a body on
its axis. The Earth rotates or spins on its axis in an anti-clockwise
direction, from West to East through 360 degrees. It makes one complete
rotation in 24 hours. Thus, for every 15 degrees of rotation, the Earth takes
one hour which is the same as four minutes for every 1 degree.
An axis is an imaginary line joining the N
(North) and S (South) poles through the centre of the Earth.
The
rotation of the Earth is very rapid although it is difficult to feel its
motion. At the equator, every point of the Earth's surface is travelling
eastwards at about 1600 km per hour. At latitude 40 degrees, the speed is about
1280 km per hr. The Earth’s axis makes an angle of 66 ½ degrees with the plane
of its orbit. In other words, the axis is tilted 23 ½ degrees from the
perpendicular.
 |
| Rotation of the Earth |
It
makes one complete rotation after every twenty four hours or one day.
The
following observations illustrates the earth’s rotation from west to east.
1. When
traveling in a fast moving vehicle we notice trees and other objects on both
sides of the road moving in the opposite direction. This observation is similar
to the movement of the earth’s rotation to the sun.
2. At
night most of the stars appear to move across the sky from east to west. This
shows that the earth is moving from west to east.
3. Sunrise and sunset: the sun rises
over the eastern horizon in the morning and sets over the western horizon in the
evening. But since the sun is in the centre of the solar system and the fact
that it does not move, this shows that the point of observation (the Earth) is
moving by rotation from West to East.
4. Day and Night: During the Earth's
rotations some regions face the sun while others do not face it. The regions
facing the sun experience day time whereas the regions which are not facing the
sun are in darkness (night). If the Earth was not rotating, one half of the
Earth would be having daylight while the other half would be in total darkness
forever. The occurrence of day and night proves that the Earth is rotating.
5. Photographs of the Earth taken from
the satellite at different times of the day show that different parts of the
Earth experience daylight at different times. If the Earth was not rotating,
different photographs taken at any time of the day would all look alike.
 |
Day
and night
|
Significances of Earth's Rotation
The
rotation of the Earth is very important because it causes the following
phenomena:
1. Alternation of day and night: Rotation of the Earth causes the
side of the Earth which face the sun to experience daylight which is the day,
whereas the side that is not facing the sun at that time will be in darkness
(night). This ensures that, at any time of the day, one half of the Earth is in
darkness and the other is in daylight. If the Earth did not rotate then its one
half would be in daylight while the other half would be in darkness all the
year round.
2. Occurrence of tides: Tides are the periodic rise and
fall of sea levels caused by the combined effects of the gravitational forces
exerted by the moon and the sun on the rotating Earth.
3. Deflection of winds and ocean currents: As the Earth rotates on its axis
from West to East, winds and ocean currents flowing over the Earth’s surface
are deflected. The anticlockwise rotation of the Earth deflects prevailing
winds to the right in the northern hemisphere and to the left in the southern
hemisphere.
4. Time difference between longitudes: The rotation is responsible for the
difference in time between different places on Earth. It causes the difference
of one hour in every 15 degree interval between longitudes, which is equivalent
to 4 minutes for each degree of longitude.
 |
Deflection of winds and ocean
currents
|
REVOLUTION
Is the movement of one body around another.
Earth’s revolution:-
·
Is
the movement of the earth around the
sun
·
The
earth takes 365
1/4 days for a complete revolution
· When the earth takes 366 days
to accomplish one revolution is
called a Leap year
·
The
earth revolution revolve around the sun in
an elliptical
· Due to the shape of the earth’s orbit, the earth is very closer
to the sun one point of the year
than at another
APHELION AND PERIHELION
Aphelion is
the furthest position of the earth’s orbit from the sun
- The earth is at Aphelion each
year on 4th July when
it is in 152 million kilometers from the sun.
Perihelion is the nearest position
of the earth from the sun
- The earth is at perihelion
each rear on 3rd January when it is 147.3 million kilometers from
the sun. Therefore the speed of
revolution is about 29.66 km per second.
 |
Earth Revolution
|
The Effects
of Earth’s Revolution
The revolution of
the Earth around the sun and the inclination (tilting) of its axis results in
the following:
1. The
four seasons of the year, namely summer, autumn, winter and spring. A season is
one of the distinct periods into which the year may be divided.
2. Change
in the altitude of the midday sun at different times of the year at any place.
3. Varying
lengths of the day and night at different times of the year. The axis of the
Earth is inclined to its elliptical plane at an angle of 66.5 degrees. If the
axis of the Earth was vertical, the sun rays would always be overhead at the
Equator, thus all places on the Earth would always experience 12 hours of
daylight (day) and 12 hours of darkness (night).
4. The
eclipses (eclipse of the sun and eclipse of the moon).
SEASONS
Season
is one of the four periods of the
year separated from each other by different
temperature conditions The seasons are
summer, autumn, winter and spring They are more pronounced between 23°c and 66°c of latitudes At the equator the year
is divided between hot and wet seasons while at the poles is very cold all the year around and the season cannot
be identified easily.
The
Northern hemisphere summer months are May, June and July. Autumn months are August,
September and October; Winter Months are November, December and January while spring months are February, March and April. In the Southern Hemisphere
summer months are November, December and January, autumn months are February, March and April Winter has May, June and July while spring
months are August, September and
October.
CAUSE
OF SEASONS
Seasons
are caused by inclination of the earth’s
axis and the earth’s revolution around the sun The earth’s axis is tilted at an angle of 660 to the earth’s
orbital plane and it is always pointing
to the same direction in space.
In its revolution around the sun
one of the hemispheres is inclined towards the sun to one period of the year
and away from it at another period of the year.
 |
Seasons of the year
|
ECLIPSE
This is the movement
of one heavily body between the two others, such that it casts shadow over the other. The eclipse involves three heavily bodies namely; the Sun, the Earth and the Moon. So long as the sun is the central both- of the solar system, it never moves, only the earth and the moon are in the motion all the time.
An eclipse is said to be total eclipse when the
whole body is obscured i.e completely blocked from the sunlight and it is described as a partial eclipse when the only part of the body becomes obscured. At any place an eclipse will last short time,
hardly seven minutes because both the earth
and the moon are in motion.
Types of Eclipse
There
are two types of eclipse i.e Lunar
eclipse and solar eclipse
1. LUNAR ECLIPSE (ECLIPSE OF THE MOON)
This
occurs when the earth moves between the sun and the moon, this casting its shadow over the moon.
 |
| Lunar Eclipse |
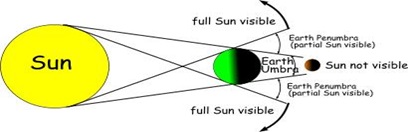
2. THE SOLAR ECLIPSE
The solar eclipse is also known as
the eclipse of the
sun. This occurs
when the moon passes between the
earth and the sun casting its shadow over the earth.
 |
| Solar Eclipse |
- Umbra or total
eclipse is when the whole body is obscured i.e completely blocked from the
sun’s light.
- Penumbra or partial eclipse is when only part of the body becomes obscured.
- Penumbra or partial eclipse is when only part of the body becomes obscured.
THE APPARENT MOVEMENT OF THE OVERHEAD SUN
The apparent movement
of the overhead sun is related to the different positions of the earth
on its movement as it revolves around the sun. The overhead
sun appears to move northwards and
south wards in an osculating
(swinging) manner.
However
the overhead sun’s northward limit is latitude 23°N People beyond this latitude never see the sun vertically above their head.
The latitudes 23°N is known as Tropical
of cancer. Similarly the overhead sun ends
23°S in its apparent Southward movement. This latitude is known as the Tropic of Capricorn on 2l June the sun is vertically
overhead on the Tropical of cancer.
This is known as the summer
solstice in the Northern hemisphere.
On 22nd December the sun is vertically
overhead on the Tropic of Capricorn this is the winter solstice in the Northern Hemisphere.
Solstice means equal night or
is when the sun on these days appears to stand still between its northward and
southward journeys.
THE SOLSTICES
The sun is overhead twice a year
at the equators 21st March
and 23rd September. 21st March is known as the spring equinox and
23rd September is known as
the autumn equinox in the Northern Hemisphere. Equinox means
equal nights, at equinox the length of day and night is equal over all places on the earth’s surface. Viewed from the Southern Hemisphere the solstices and the equinoxes are reversed.
LENGTH OF DAY AND SIGHT
Places
along the equator experience equal day and night all the year, but northwards
or south wards towards the poles. The length of day and night varies
with latitudes. For instance in
Northern Summer when the Northern Hemisphere is inclined towards the sun, days are longer than nights. However at latitude 66°N known as the Arctic. Cycle and beyond
the sun appears around the sky without
setting in the North Pole daylight is experienced
for six months before the sunset.
Then this region remains in
darkness for the next six months; Latitude 66° south is known as the Antarctic cycle. The Polar
Regions south of the Antarctic cycle experience the long six months night from March to September and the six months day light from October to February.
PARALLELS AND MERIDIANS
Parallels
are more commonly known as latitudes.
Latitude refers to the angular distance North or South
of the equator calibrated in degrees, minutes and seconds, measured from the
centre of the Earth. The equator is given a value of 0º. It is an
imaginary line which divides the Earth into two hemispheres (northern
hemisphere and southern hemisphere). The Northern hemisphere has latitude of
90ºN and the Southern hemisphere has latitude of 90ºS. All other latitudes are
drawn north or south, parallel to the equator. A particular latitude, say 60ºN
joins all points on the surface of the Earth which make an angle of 60º from
the centre of the Earth (the equator). Any circle drawn around the Earth,
parallel to the equator, is a parallel of latitude. Table 1.3 shows important
parallels and figure 1.18 shows the location of these parallels on the Earth’s
surface.
Latitude
Parallel
Meridians are commonly known as longitudes.
A longitude is an imaginary line drawn on the map from the North Pole to the
South Pole. Meridians are numbered in degrees East or West of longitude 0°,
called Greenwich Meridian (because it passes through a town in England
called Greenwich). It is also known as the Prime Meridian because it is
the line of reference from which all other meridians are established.
A
longitude, therefore,
refers to angular distance measured in degrees East and West of the Greenwich
Meridian. The Prime Meridian runs through the poles and the
Greenwich observatory near London. All lines of longitude are in equal length
and divide the Earth into two equal semi circles. There are 360° in a circle,
with 180° lying east of the Greenwich Meridian and the other 180° west of
Greenwich.
The
Greenwich line has been chosen by convention (meaning that any other line could
have served the same purpose).
Longitude/Meridian: Is angular distance measured in degrees East or west of the prime meridian, the run from north to south.
 |
| Longitudes and Latitudes |
The importance of parallel and meridians
Longitudes and
latitudes are very important to any geographer or map reader. The importance of
longitudes and latitudes include the following:
1. They
are used by pilots and sailors to guide their paths as they steer the planes
and ships.
2. When
used together, longitude and latitude define a specific location through
geographical coordinates (Fig 1.23).Each location on Earth has its unique
latitude and longitude. For example, the location of a point shown on figure
1.23 below is 40°N,60°W.
3. Longitudes
enable geographers to calculate the local time of a place, X, given the local
time and longitude of place Y, as the point of reference..
4. Latitudes
are used as a guide to explain the variation in climate on the surface of the
Earth. It is generally known that places along the equatorial belt experience a
hot and wet climate for most of the year. As you move north or south of the
equator, the climate progressively become cold. Places at the north and south
poles are extremely cold and are covered by ice and snow throughout the year.
LATITUDE AND LONGITUDE
Latitude: Is the angular
distance north or south of the equator measured in degrees,
minutes and seconds. Also can be
defined as the lines drawn on a map from east to west.
- The
equator is latitude of 0°
- The
equator divides the earth into two equal parts (Hemisphere)
- The
hemisphere north of the equator is northern hemisphere
- The
hemisphere south of the equator is known as Southern hemisphere
- Latitude
are also known as a
parallel lines of equator because they never meet.
- The lines of latitude are
measured from 0° (the equator) to 90° north and south.
Lines of Latitude are;
·
The equator 0°
·
The tropical of cancer 231/2°N
·
The Tropical of Capricorn 231/2°S
·
Arctic cycle 661/2°N
·
Antarctic cycle 661/2°S
PARALLEL
OF LATITUDE
30°N
Longitude
Is an
angular distance measured in degrees east or west of the prime meridian, they
run from north to south.
Greenwich is a longitude 0°. It is also
known as prime meridian. The prime meridian is the line running through the
poles (North and South) and is known as Greenwich 0°. Longitudes are measured
from 0° to 180° East or West of Greenwich, all meridians are passing through
the North and south poles.
LONGTUDE AND TIME
The
earth rotates on its own axis from west to east once every twenty-four hours
(one day). This means that the earth turns through 360° in twenty-four hours.
All places along a given meridian will experience midday along the same
meridian, it is known as Local Mean, on the Greenwich meridian is known as
Local Mean Time (LMT).
When
it is 12:00 noon; on the Greenwich meridian it will be 1:00 pm at a place of
15°E or 11:00 at a place of 15°W. To
find time for example for Musoma
in Tanzania (34°) when it is 12:00 in Kinshasa Zaire
1.
Note
the 1onitude position of Kinshasa 15°30°E and Musoma 34°
2.
Find
the difference in degree of longitude between Kinshasa and Zaire 34° 15°30 = l81/2
3. Find the difference in time between
Kinshasa and Zaire
4. Since
Musoma is to the east of Kinshasa, Musoma time will be ahead of that
of Kinshasa by 1 hour and
14 minutes therefore time for Musoma will be 12:00 + 1:14 =
13:14 pm Or 1:14 pm.
In the other hand given the time difference between two places and the longitude of one of them,
one can calculate the longitude position
of the second places Kinshasa 15° 30° and 1 hour and 14
minutes. Behind the time of Musoma.
Find the longitude position of Musoma
Difference in time between Musoma and Kinshansa 1
hour and 14 minutes.
Difference
in degrees of longitude between Musoma and Kinshansa is lhr and 14 minutes =
74/4 or 18°30°
Since the time of Kinshasa is behind that of Musoma, Musoina must be east of Kinshansa. Therefore the longitudinal position of Musoma will be 15°30´ + 18°30´ = 34°E.
GREAT CIRCLE
The
intersection of the surface of a sphere
and a plane through its centers for example meridians of
longitude and equator e great circle in the earth’s surface. Therefore
there is no limit to the number of
great circle that can be drawn.
 |
| Great Circle |
Great circle also is a circle drawn
on a globe (or other sphere) with a center that includes the center of the globe. Thus a great circle divides the
globe into two equal halves.
IMPORTANCE
OF GREAT CIRCLE
1. The
great circles are important for aero planes which use them as route ways to guide their path
2. Great circles are important for ship to follow routes along great
circles
TIME
Refers
to a period that is used for a event or activity. It is measured in seconds,
minutes, hours, days, months or years.
TIME ZONES
Is the
region having the same standard time, Standard time is common on time for all
countries belonging to the same time zone for example; Tanzania, Kenya, Uganda,
Ethiopia, Djibouti and Somalia use the same standard time. This is commonly
referred to the East African Standard time.
There
would be problems of telling time if every place had its own time set according
to local mean time. For example, there would be great confusion in railway and
airway timetable or in radio programs if they had to show difference time each
one place within a small area. To avoid this problem, different stretches of
land take their time from great Meridian. The time adopted is known as STANDARD TIME.
In
East Africa, standard time is taken from meridian of 45ºE when a whole stretch
of land keeps to the same standard time that stretches from a time zone.
Therefore time zone refers to a stretch of land where standard time is accepted
through out a longitudinal zone 15° width. Countries with large stretches of
land have several standard time zones. There are 24 time zones in the world.
The Greenwich Meridian is the starting point for dividing the globe into 24
time zones, the standard time for Greenwich is known as the
Greenwich Mean Time (GMT)
Essence of Time Zone
In a certain place there could be a place
on the surface using its’ own
local time. This would brought a lot of confusion example every radio station would have to announce different times for every
region within the same country: Local time
of Bukoba would be different from that of Dodoma.
- The above confusion was avoid when it was internationally agreed to split the world into 24 time zone according to Longitudes
- The
longitudinal division across the earth with an approximates
with of 15 of longitude which is regular across the oceans.
- Each
time zone has a standard time which is the time of the longitude (meridian near the center of time zone. In the same way, all countries belonging to the same time zone
have common time.
Note: Large
countries like Canada, USA and
Russia have different standard times for
different regions within them because they are crossed by many time zone.
Exercise
5
1. If
it is 9:30 am at
Kasse 33°15°E what time is in
Zanzibar 45°15°E?
2. Find
the time for the Youncle 30°w if it
is 12.00 noon London
3. When
it is 3.30 pm at Nairobi (25°E) what
is the time for Comoro 120°E?
INTERNATIONAL DATE LINE.
The
line where date is changed or where the calendar day begins.
One
travels eastwards and cross the date
line, one will gain a day, if one
travels westwards and cross the date line, one will lose a
day, if Greenwich it is noon on
Tuesday a place 90°W would be 10 am on
Tuesday, at a place 180°W it would be midnight Monday. On the other hand a place 90°E would be 6.00pm on Tuesday and at a place 180°E would be midnight on Tuesday.


















Hello, the notes are very clear and illustrated
ReplyDeleteThank you
In ordinary year earth takes 366¼ days to complete one revolution.
ReplyDeleteIs there any ¼ day?, If Yes verify it with a critical explanation and relevant example.
ordinary year has 365 1/4 days. 1/4 day is added after 4 years to make a leap year of 366 days
ReplyDeleteThank you indeed...
ReplyDeleteWould you edit these notes again