JOIN US WHATSAPP
CLICK HERE
JOIN US TELEGRAM
CLICK HERE
TOPIC 4: CLASSIFICATION OF LIVING THINGS
Concept of Classification
The Concept of Classification
Explain the concept of classification
Have you ever visited a library? How are the books arranged and kept? Are they arranged randomly or systematically? Obviously the books are arranged systematically in the shelves. Science books are kept separately in their respective shelves. Science books are kept separately from social or commercial books. Biology books are separated from physics books or chemistry books. Likewise, in the shop, laboratory or pharmacy items are sorted and placed on the basis of their similarities.
In the world, there are numerous varieties of living organisms.These organisms do vary in size, structure, shape, habitat, mode of feeding and even mode of reproduction. The organisms can be sorted out and placed into different groups based on their similarities. The system of sorting out and placing organisms into different groups on the basis of their similarities and differences is called classification.
The Importance of Classifying Living Things
Explain the importance of classifying living things
The following are importance of classification
- Classification makes the study of living things easy
- Classification makes communication easy among biologists from different parts of the world
- It provides good organized system in which a newly identified organism can be easily fitted in future.
- It makes it easier to identify organisms
- It can be used to predict characteristics that are present in the members of the same group.
Classification Systems
Major Groups of Living Things
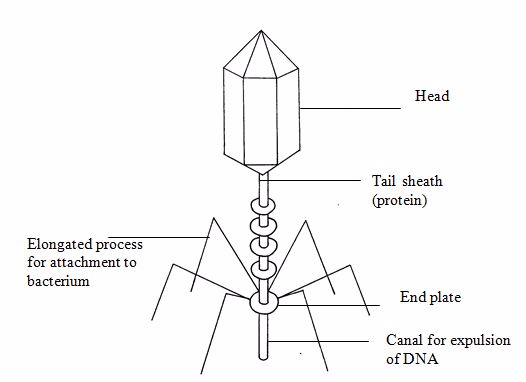
Viruses
Viruses were discovered by a Russian botanist D. I. Ivanovsky and a Dutchman Beijerink. In 1852 Ivanovsky prepared an infectious extract from tobacco plants that were suffering from mosaic disease. When the extract was passed through a filter able to prevent the passage of bacteria, the filtered fluid was still infectious. 1898 Beijerink gave the name “virus” (in latin means, “poison”) to describe the infectious nature of certain filtered plant fluids.
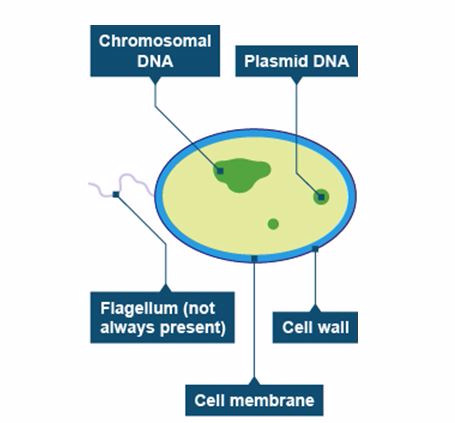
Kingdom Monera
Kingdom Protoctista
Phyla of the Kingdom Protoctista
Mention phyla of the kingdom protoctista
The phyla of kingdom protoctists include the following:
- Euglenophyta e.g. Euglena
- Rhizopodia e.g. Amoeba
- Zoomastigma e.g. Trypanosoma
- Apicomplexa e.g. Plasmodium
- Oomycota e.g. White root
- Chlorophyta e.g. Spyrogyra
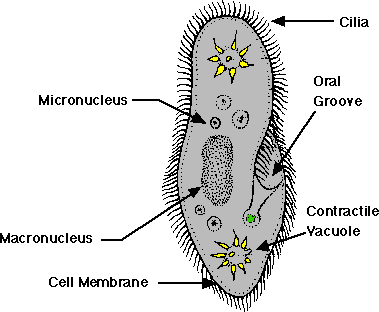
- Cilliaphora e.g. Paramecium
- Rhodophyta e.g. Red algae
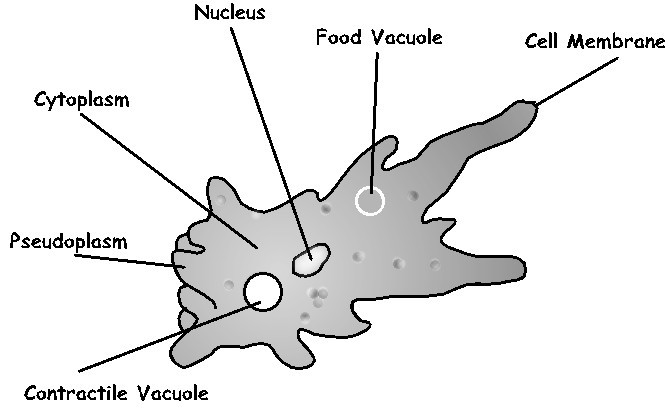
Structure of Amoeba and Paramecium
Describe structure of amoeba and paramecium
Amoeba belong to phylum Rhizopoda, organisms with the following extra features:
- They are eukaryotes
- Unicellular
- Parasitic
- They move using pseudopodia
Pseudopodia are projection of the cytoplasm that extend and pull the amoeba forward or engulf food particles.


The Advantages and Disadvantages of Amoeba, Euglena Paramecium and Plasmodiu
Explain the advantages and disadvantages of amoeba, euglena paramecium and plasmodium
Advantages of Paramecium: Are eaten by small water animals
Disadvantages of Paramecium: Causes diseases of bulanterdium eoli destroying the lining of intestines
Osmoregulation:Paramecium has two contractile vacuoles and each is associated with permanent system of collecting channels, which empty, into the main vacuole.
Feeding: Paramecium feed on bacteria. These are obtained from the surrounding water by the beating of the cilia-lining o the oral grove.
Reproduction:Paramecium reproduces both asexually and sexually. The asexual method is more common and it is binary fission. Sexual method is called conjugation.
Movement in paramecium is caused by cilia beating. This movement is called cilliary movement.