TOPIC 4: MULTIMEDIA
Multimedia Concepts
The Historical Development of Multimedia
Explain Historical Development of Multimedia
Today multimedia might be defined as the seamless digital integration of text, graphics, animation, audio, still images and motion video in a way that provides individual users with high levels of control and interaction. The evolution of Multimedia is a story of the emergence and convergence of these technologies.
- Visionaries: From the ingenious idea of the programmable computer, trace the innovations of the outstanding thinkers that had a direct impact on the explosion of the technological age.
- Text, Processing and Software: Inventions and innovations that spawned the development of software enabling computers to move from mathematical processing to technology that creates and delivers multi media.
- Computers: From the printing press through the exclusive military and academic and corporate worlds trace computer development into the ubiquitous role of the desktop personal computer of today.
- Audio & Communication: From the telegraph signal to cellular telephones, follow the development from signal transmission to digital transmission of voice
- Video & Animation: From manually manipulated negative film and hand drawn sketches, video and animation develops to sophisticated digital creation and rendering of motion
Therefore, Multimedia is content that uses a combination of different content forms such as text, audio, images, animations, video and interactive content. Multimedia contrasts with media that use only rudimentary computer displays such as text-only or traditional forms of printed or hand-produced material.
Multimedia can have a many definitions these include
- Multimedia means that computer information can be represented through audio, video, and animation in addition to traditional media Or
- Multimedia is the field concerned with the computer-controlled integration of text, graphics, drawings, still and moving images (Video), animation, audio, and any other media where every type of information can be represented, stored, transmitted and processed digitally.
Graphics
These are visual images or designs on some surface, such as a wall, canvas, screen, paper, or stone to inform, illustrate, or entertain. In contemporary usage it includes:
- A pictorial representation of data, as in computer-aided design and manufacture,
- In typesetting and the graphic arts, and in educational and recreational software.
Images that are generated by a computer are called computer graphics. Computer graphics are pictures and films created using computers. Usually, the term refers to computer-generated image data created with help from specialized graphical hardware and software.
COLOR DEPTH
- The number of distinct colors that can be represented by a piece of hardware or software. Color depth is sometimes referred to as bit depth because it is directly related to the number of bits used for each pixel. A 24-bit video adapter, for example, has a color depth of 2 to the 24th power (about 16.7 million) colors. One would say that its color depth is 24 bits.
- Also known as bit depth, is either the number of bits used to indicate the color of a single pixel, in a bitmapped image or video frame buffer, or the number of bits used for each color component of a single pixel. For consumer video standards, such as High Efficiency Video Coding (H.265), the bit depth specifies the number of bits used for each color component
Comparison: same image on five different color depths (bits). Different looks (color/greyscale/black-and-white … dithering), but also different file sizes.

32bits.png;4,294,967,296 colors;98KB

8bits.png;256 colors;37KB(-62%)

4bits.png;16 colors;13KB(-87%)
IMAGE SIZE
- The width and height of a bitmapped image, measured in pixels.
- The size of a graphics file, measured in bytes.
Image dimensions are the length and width of a digital image. It is usually measured in pixels, but some graphics programs allow you to view and work with your image in the equivalent inches or centimeters. Depending on what you plan to use your image for you may want to change the image size. For example, if you are using a high-resolution digital photograph, you may want to make the image dimensions smaller for publishing to a Web page. When using a graphics or image-editing program, you will usually have two options for changing the image dimensions: resize or resample.
JOIN US WHATSAPP CLICK HERE
JOIN US TELEGRAM CLICK HERE
Multimedia Devices
Sound and Video
Video Recording / Shooting
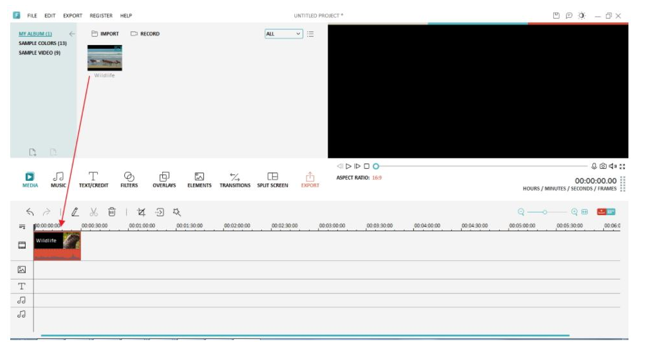
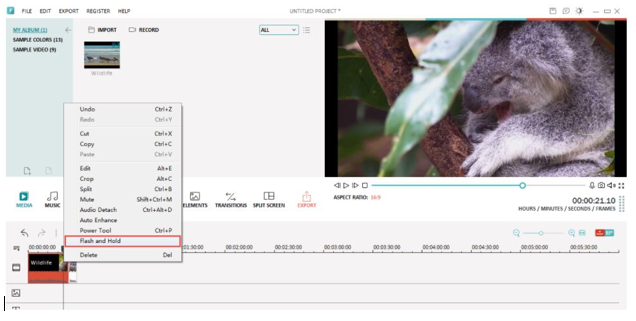
Video Editing
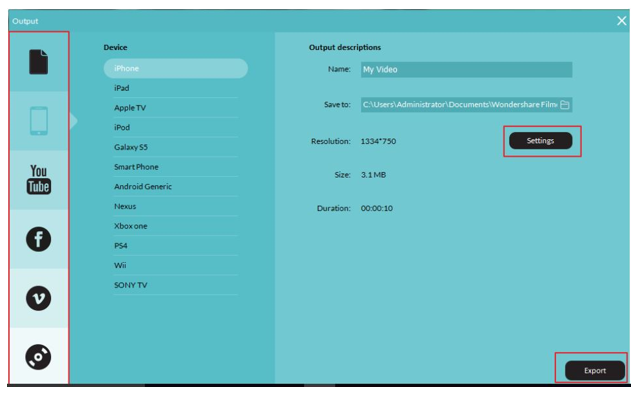
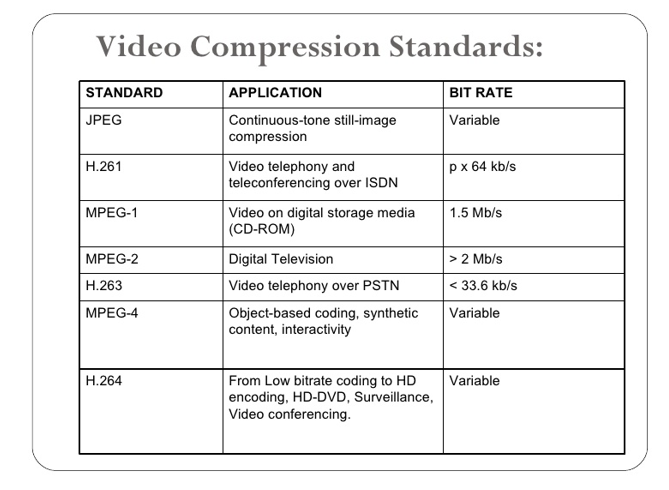
Video Compression





1 Comment
this program is really enormous it helps as students alot keep it up