TOPIC 4: RATES AND VARIATIONS
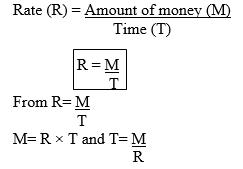


Rates
A rate is found by dividing one quantity by another.
Rates of Quantities of Different Kinds
Relate rates of quantities of different kinds
For example a rate of pay consists of the money paid divided by the time worked. If a man receives 1,000 shilling for two hours work, his rate of pay 1000 ÷ 2 = 500 shillings per hour. From the above example, we find out that
Example 1
1. A man is paid 6,000/= for 8 hours work.
- What is his rate of pay?
- At this rate, how much would he receive for 20 hours work?
- At this rate, how long must he work to receive 30,000 shillings?
Solution:


Quantities of the Same Kind
Relate quantities of the same kind
Example 2
A student is growing plants she measures the rate at which two of them are growing. Plant A grew 5cm in 10 days, and plant B grew 8cm in 12 days. Which plant is growing more quickly?
Exercise 1
1. A woman is paid 12,000/= for 8 hours work.
Converting Tanzanian Currency into other Currencies
Convert Tanzanian currency into other currencies
Different countries have different currencies. Normally money is changed from one currency to another using what is called a Rate of Exchange.
This makes trade and travel between countries convenient.
Conversion of money is done by multiplying or dividing by the rate of exchange.
Eg. If at a certain time there are 1,100 shillings to each UK pound (£), to go from £to shillings, multiply by 1,100, and to go from shillings to £divide by 1,100.
NB: The rate of exchange between two countries varies from time to time.
Example 3
Suppose the current rate of change between the Tanzanian shillings and the Euro is 650 Tsh per Euro.
- A tourist changes 200 euros to Tsh. How much does he get?
- A business woman changes 2,080,000 Tsh to euros. How much does she get?
Exercise 2
At a certain time there are 600 Tsh to one US dollar ($).
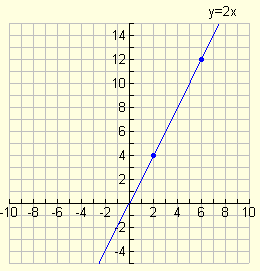
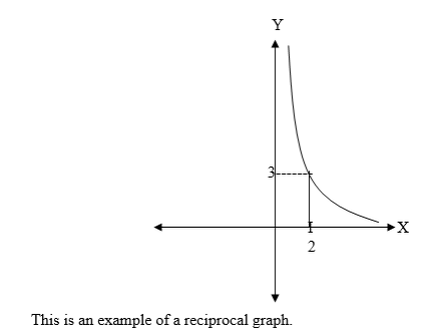
Variations


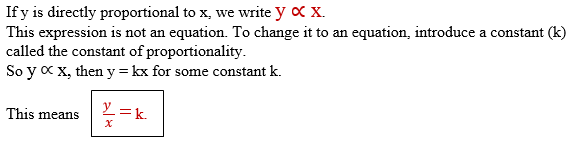
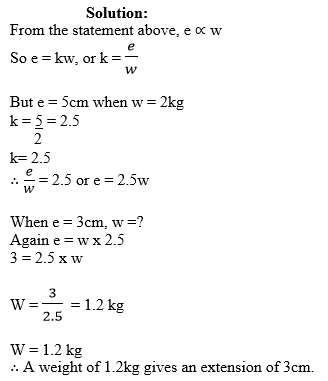
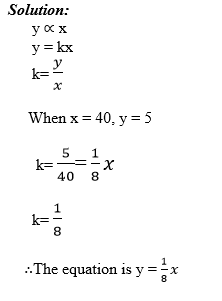

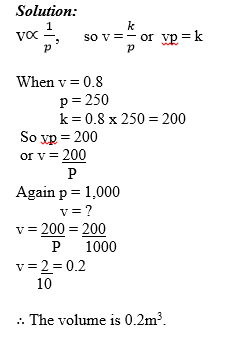
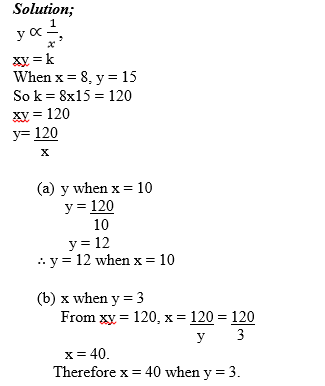


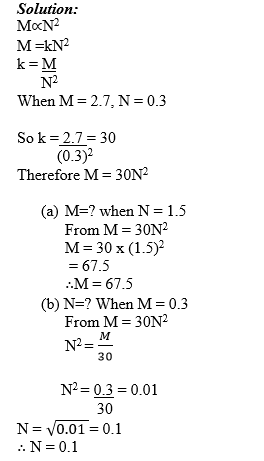
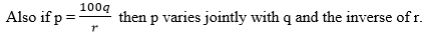
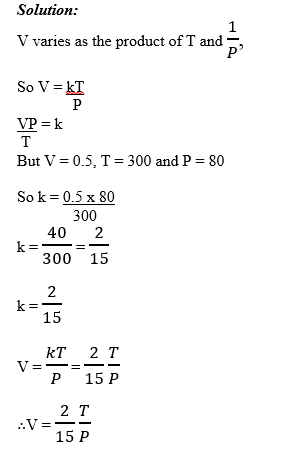
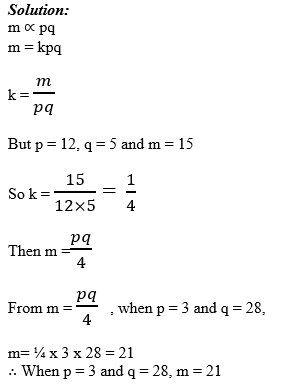



1 Comment
Thanks your notes are very useful to me.!!