JOIN US WHATSAPP
CLICK HERE
JOIN US TELEGRAM
CLICK HERE
TOPIC 6: STRUCTURE AND PROPERTIES OF MATTER
Structure of Matter
State of matter is defined in terms of the phase transitions which indicate the change in structure and properties. Solids, liquids and gases all are made up of microscopic particles. The behavior of all these particles also varies in three phases.
The Concept of Matter
Explain the concept of matter
Matter is anything that has mass and occupies space. In other words, matter is anything that has weight and volume. For example, stone is considered a matter because it has mass and it occupies space. Therefore, everything we see around us is considered a matter.
The Particular Nature of Matter
Justify the particulate nature of matter
Matter is made up of tiny particles. These particles are either atoms or molecules. That is to say atoms or molecules combine in millions to form matter. Atoms or molecules are combined in chemical reactions to form matter.
Atom is a smallest part of an element that can take part in a chemical reaction. When two or more atoms combine they form a molecule.
The nuclear attractive forces are responsible for holding atoms together in a matter. Some matters have strong attractive nuclear forces between atoms e. g gold, silver, iron. Some matters have weak attractive forces between atoms e. g water, oxygen gas.
The Kinetic Theory of Matter
Explain the kinetic theory of matter
The Kinetic Theory of matter describes the physical properties of matter in terms of the behaviour of its component atom or molecules. It states that
“All matter is made up of very small particles that are in constant motion”
This theory tells us about two important things;
- That matter is a combination of tiny (very small) particles.
- And all these tiny particles are always in motion.
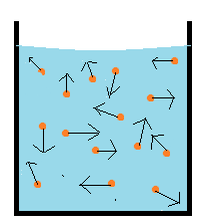
The motion of the particles in a matter was experimented by a scientist known as Robert Brown in an Brownian motion experiment.
Brownian motion
This was an experiment conducted by a scientist Robert Brown to investigate the motion of the tiny particles in a matter.
In his experiment, he put pollen grains in water and observed them using a microscope. He observed that, pollen grains were moving in a random or irregular motion.

Brownian movement
Mr. Brown discovered that, the random motion of the pollen grains in water was caused by the collisions between them and the molecules of water. The pollen grains continued with the random motions since the collisions did not stop.This motion is called Brownian motion.
Brownian motion is an irregular motion of tiny particles suspended in a fluid.
Three States of Matter
Classify three states of matter
There are three states of matter, namely:
- Solid state
- Liquid state
- Gaseous state
Solid state is the state of matter, which include materials in which the inter-molecular force between molecules are greatest and distance between molecules is small. Solids have definite shape and volume. Particles in solid are closely packed together. Examples of solids are wood, iron, glass, rubber, concrete etc.
Liquid state includes substances in which the inter-molecular forces are low compared to solid state, there is greater distance between one molecule and another. Solid shave no defined shape or volume but they take the shape and of the container or vessel. Examples of liquid substances are water, honey, spirit, kerosene, and petroleum.
Gaseous state is the state of matter in which there is no intermolecular forces between molecules hence molecules are free to move from one place to another. Gases have no defined shape or volume but they fill the whole container in which they are kept. Particles in gases are most free compared to solids and liquids. Examples of gases are hydrogen, oxygen, carbon dioxide gas.
Difference between solid state, liquid state and gaseous state of matter
| Solid state | Liquid state | Gaseous state. |
| It concerns with solid matter | It concerns with liquids/ fluids matter | It concerns with gases |
| Have high intermolecular | Low intermolecular force | No intermolecular force |
| No distance between molecules | There is little distance between molecules | Molecules are far from each other |
| Good examples are iron materials, woods etc. | Good examples are water, soda, kerosene and petrol | Good examples are oxygen and hydrogen |
Elasticity
Adhesion and Cohesion
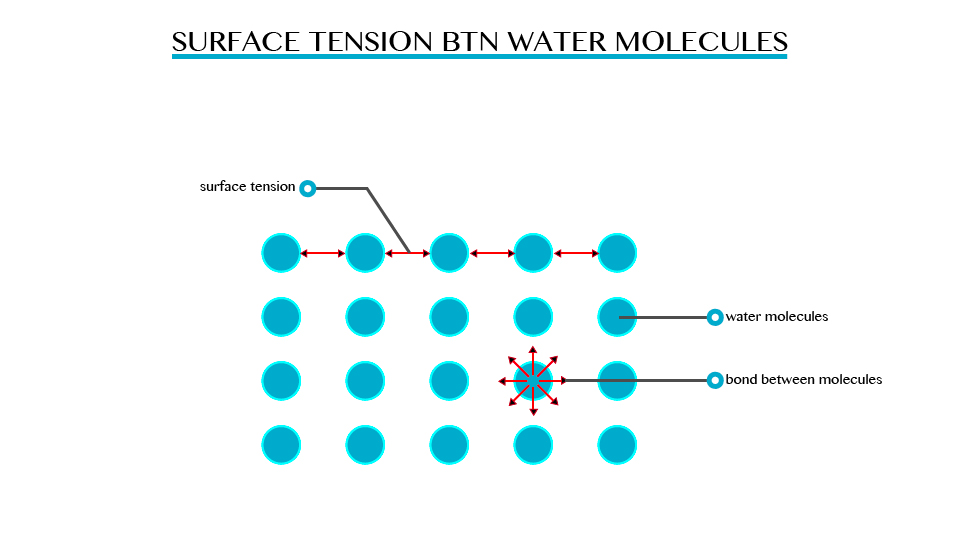
Surface Tension
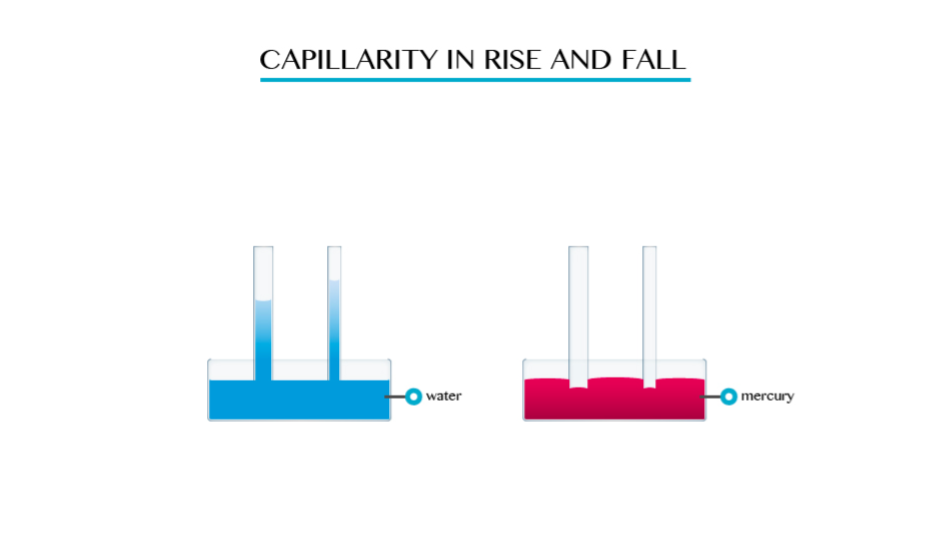
Capillarity
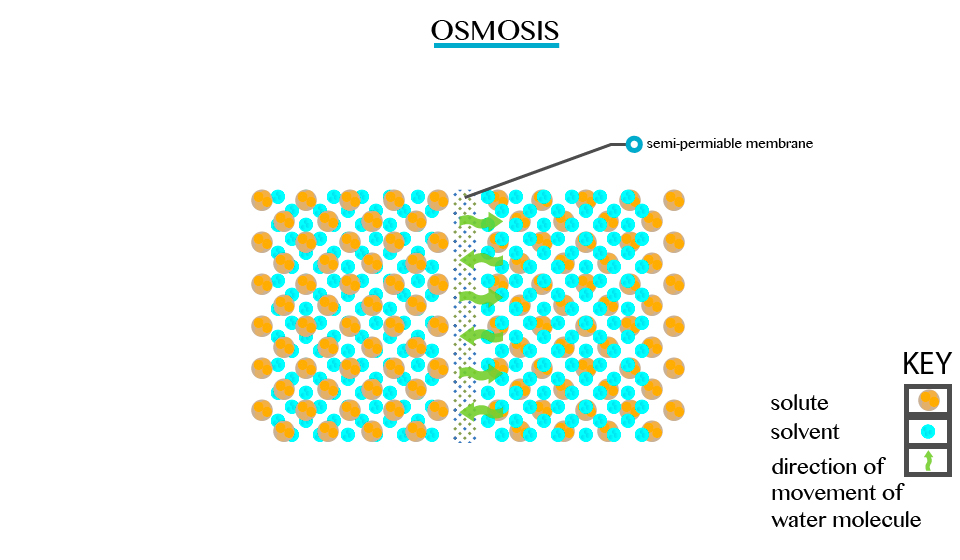
Osmosis