TOPIC 8: WORK, ENERGY AND POWER
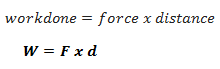
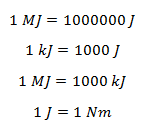
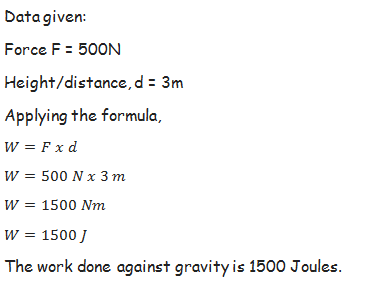

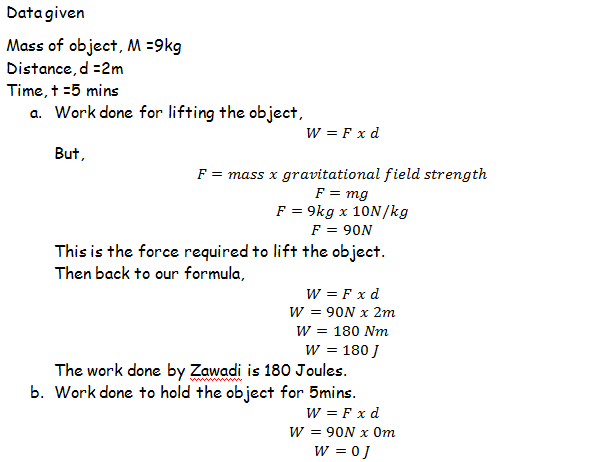
Work
The Concept of Work
Explain the concept of work
Work is said to be done only if the application of a force makes a body move from one point to another.
If a person pushes a wall and without making it move, even if the person sweat and physically become tired, he would not have done any work. But if the person pushes a trolley and the trolley moves then work is said to be done.
Work is defined as the product of the force applied and the distance moved in the direction of the force.
The S.I Unit of Work
State the S.I unit of work
Work is the product of force and distance moved in the direction of the force.
Thus,
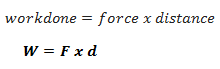
The SI unit of work done is Joule (J). Other units are Kilojoules (Kj) and megajoules (MJ) and Newton metre (Nm).
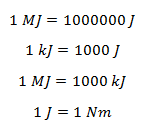
The Work Done by an Applied Force
Determine the work done by an applied force
The work will be done only if the following conditions are fulfilled; –
- There must be a force acting on a body.
- The body must move in a direction parallel to that of the applied force. That means, the direction movement of the object can be opposite to that of the applied force but parallel to it.
Therefore, work is NOT done if the force and distance are at right angle to each other (perpendicular).
Example 1
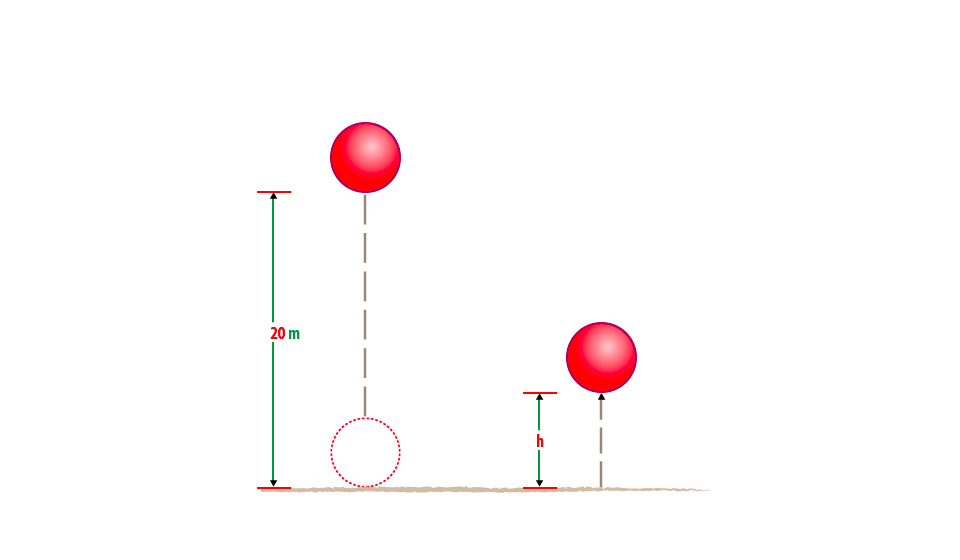
A sack of maize, which weighs 800N, is lifted to a height of 2m. What is work done against gravity?
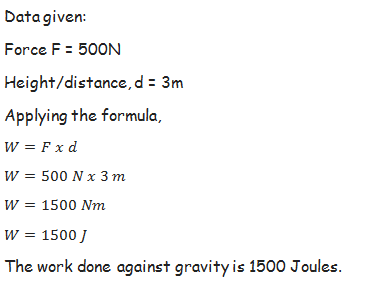
Example 2
A force of 70N pulls a box along a smooth and level ground a distance of 7m. Calculate the work done by force.

Example 3
Zawadi lifted a 9kg object 2m up and then hold it there for 5 minutes. How much work did Zawadi do for a) Lifting up the object, b) Holding the object for 5 minutes.
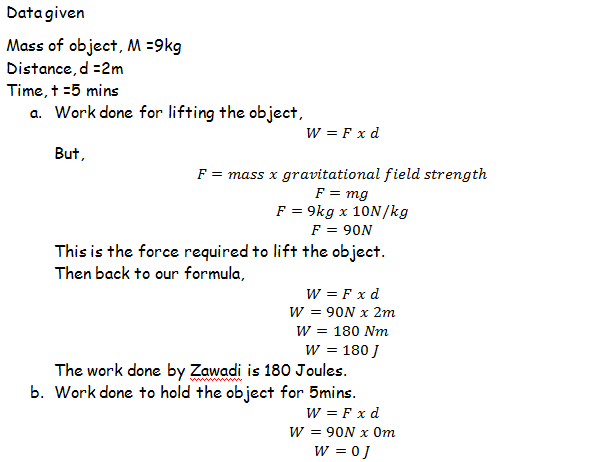
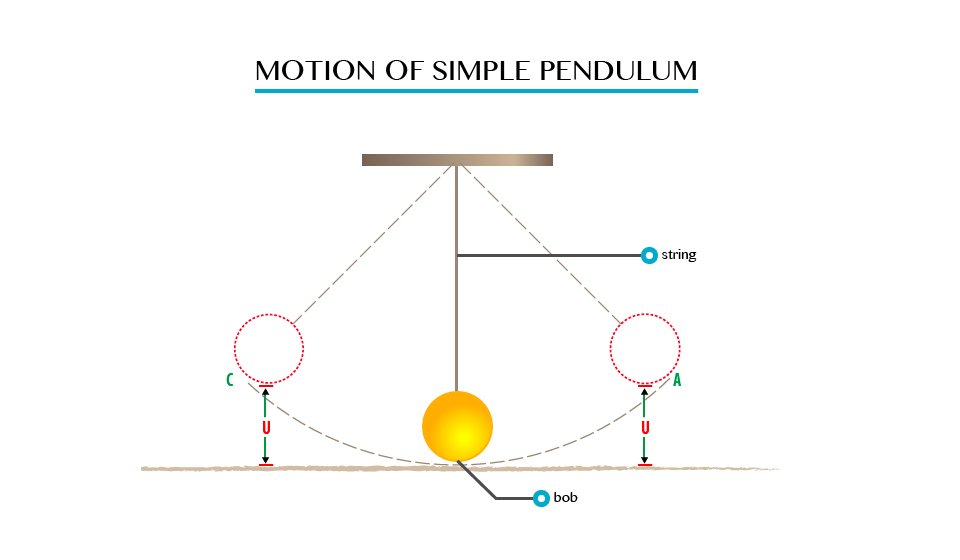
Energy
Power
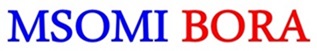


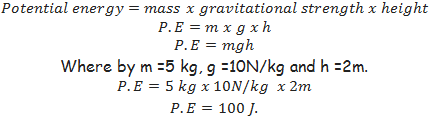


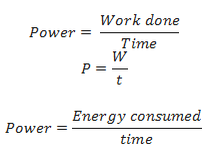
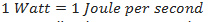
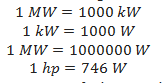
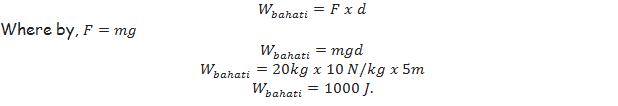
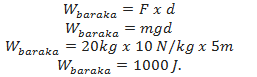
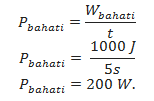
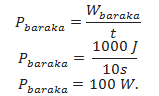
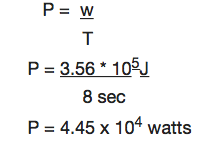
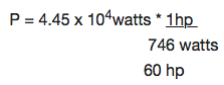

1 Comment
Physics form one past paper