JOIN US WHATSAPP
CLICK HERE
JOIN US TELEGRAM
CLICK HERE
TOPIC 3: LIGHT
Light is a form of energy which controls the sense of vision. We are able to see things because of the light coming from them.
Reflection of Light from Curved Mirrors
Difference between Concave and Convex Mirrors
Distinguish between concave and convex mirrors
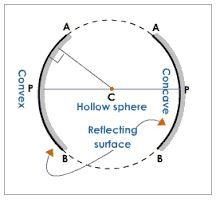
Concave mirror is a spherical mirror whose reflecting surface is curved inwards. A Good example is the driving mirror of a car.
Convex mirror is a spherical mirror whose reflective surface is curved outwards. A good example of a convex mirror is a shaving mirror.
General demonstrations of convex and concave mirrors (curved mirrors:
The Terms Principle, Axis, Pole, Principle Focus and Radius of Curvature as Applied to Curved Mirrors
Explain the terms principle, axis, pole, principle focus and radius of curvature as applied to curved mirrors
Terms used in studying curved mirrors
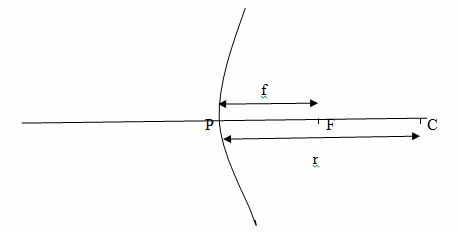
- Centre of curvature (C):the centre of the sphere of which a mirror is a part of.
- Radius of curvature (r): the radius of sphere of which a mirror is a part of. Radius of curvature is double the focal length. That is r=f/2.
- Pole (P): the central point of the reflecting surface of spherical mirror (curved or convex mirror).
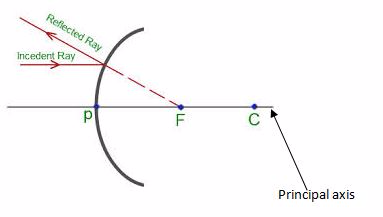
- Principal axis:the straight line joining the centre of curvature (C) and the pole (P).
- Principal focus (F):the point on the principal axis where light rays tend to intersect after being reflected. This point is between centre of curvature and the pole. In concave mirror, parallel rays to the principal axis meet at the principal focus after reflection. In convex mirror, parallel rays to the principal axis appear to originate from the principal focus behind the mirror after reflection.
- Focal length (f): the distance from the pole of the mirror to the principal focus. Focal length is half the radius of curvature.
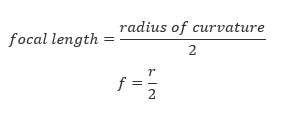
The Images Formed by a Curved Mirror
Locate the images formed by a curved mirror
Case (1)
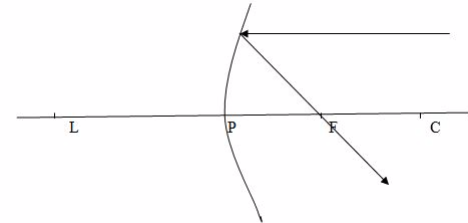
When a beam of light parallel and very close to the principal axis CL, is reflected from a concave mirror, it converges to a point F, on the principal axis called the principal focus.
Case 2
When a ray passes through the principal focus, F, it is reflected parallel to the principal axis.
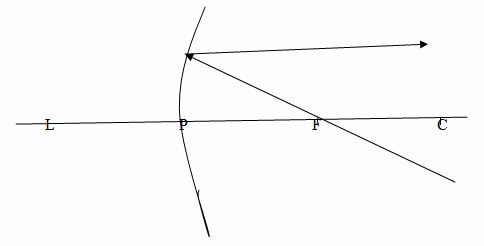
Case 3
When a ray passes through the centre of curvature, C, which therefore strikes the mirror at normal incidence, it is reflected back along its original path.
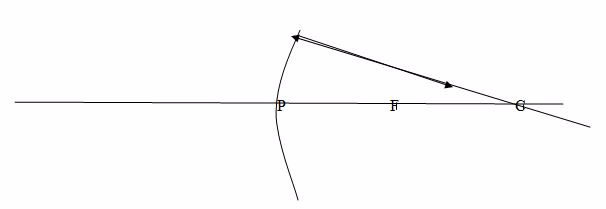
Note: Concave mirrors have a real focus because light passes through the focus.
The formation of images by concave mirror tends to change as the position of object changes.
Case 1: Image (I) formed by a concave mirror when the object is beyond C.
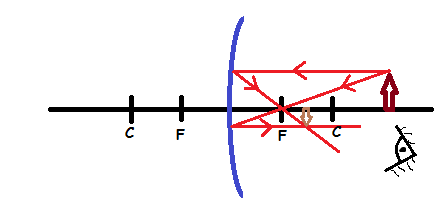
Properties of images formed:
- The image is between C and F
- The image is smaller than the object
- The image is inverted (upside down)
- The image is real
Case 2: The object is placed at C
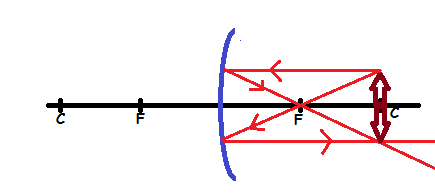
Properties of image
- The image is formed at C
- The image has the same size as object
- The image is inverted (upside down)
- The image is real.
Case 3: The object is placed between C and F
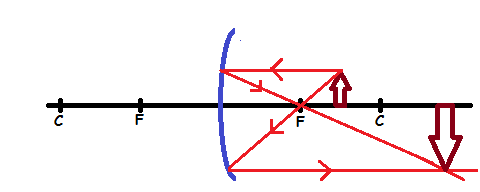
Properties of image formed
- The image is real
- The image is large than object
- The image is formed beyond C
- The image is inverted (upside down)
Case 4:The object is placed at F

Properties of image:
- The image is formed at infinity (x)
- The image is formed beyond C
- The image is large than object
- The image is Real
Case 5:The object is placed between F and P.
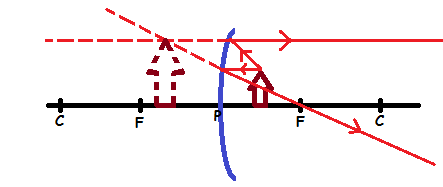
Properties of image formed:
- The image is virtual
- The images is upright
- The image is formed behind the mirror
- The image is large than the object
Formation of images in a convex mirror:
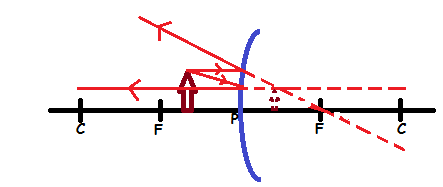
Obviously, there is only one kind of image formed when an object is placed at any position.
Properties of image formed by convex mirror:
- The image is virtual
- The image is upright
- The image is smaller than object (diminished)
- The image is formed behind the mirror.
Note: We see images of ourselves and other things through curved mirrors when they are formed behind the mirrors, virtual and upright. For the concave mirrors, images are magnified but for convex mirrors, images are diminished. All real images cannot be seen through the mirrors because they are formed in front of the mirror.
The Mirror formula
This shows the relationship between the distance of the object from the mirror U, distance of the image from the mirror V and the focal length f.

To avoid confusions the formula is used by considering a sign convention known as ‘positive-is-real convention’. In Positive-is -real sign convention the following are to be considered before applying the values into the equations;
- Real images are given a positive ‘+’ sign.
- Virtual images are given a negative ‘-‘ sign.
- Distances of real objects and images are given positive ‘+’sign.
- Distances of virtual images are given negative ‘-‘ sign.
- A real focal length is given a positive ‘+’ sign.
- A virtual focal length is given a negative ‘-‘ sign.
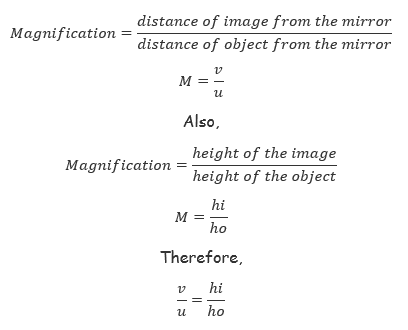
Magnification
Magnification is the ratio of the image distance to the object distance. Magnification is a unit less quantity which shows how much the image is larger or smaller to the object.
In this case, magnification is also defined as the ratio of the height of the image to the height of the object.
Example 1
An object 2cm long is erected 8cm infront of a concave mirror of radius of curvature 10cm. By using a scale drawing, determine the position, size and nature of image formed.
Data given
- Height of object, Ho = 2cm
- Object distance, U= 8cm
- Radius of curvature, r = 10cm
- Focal length,f =8cm
- Choose suitable scale.
- Say 1cm represents 5cm
From this scale then
- Height of object, Ho = 2cm
- Object distance, U= 2cm
- Focal length, F = 2.5cm
Thus,
Image distance, V = X
Image Height, H1=Y
The Focal Length of a Concave Mirror
Determine practically the focal length of a concave mirror
Focal length (f) is the distance between the principal focus and the pole.
Convex and Concave Mirrors in Daily Life
Use Convex and concave mirrors in daily life
Curved mirrors are used as:
- Driving mirrors
- Shaving mirrors
- Reflectors
Question Time 1
Question Time 2
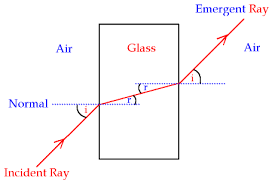
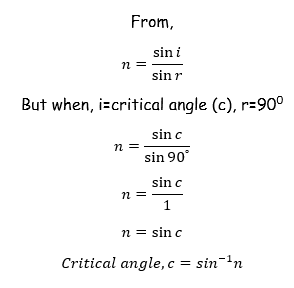
Refraction of Light
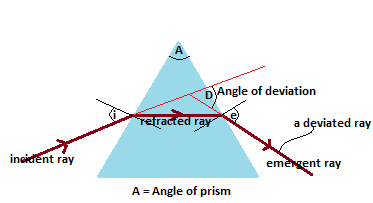
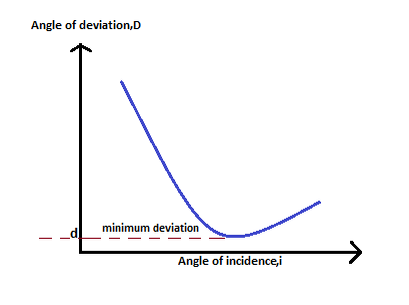
Refraction of Light by Rectangular Prism
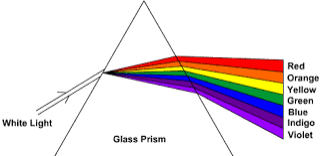
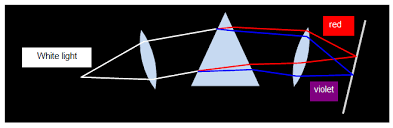
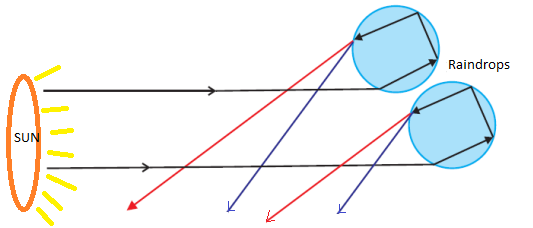
Colours of Light
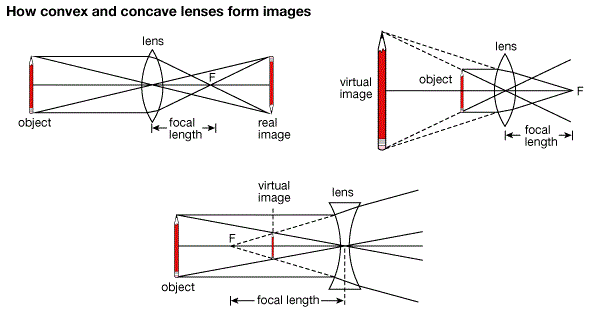
Refraction of Light by Lenses



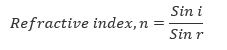
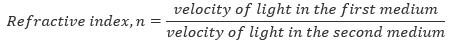
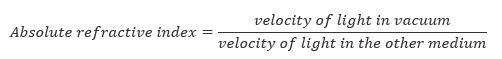



1 Comment
The syllabus coverage is quite in order.However there are a few grammatical errors that need be corrected.