JOIN US WHATSAPP
CLICK HERE
JOIN US TELEGRAM
CLICK HERE
TOPIC 4: FORCES IN EQUILIBRIUM
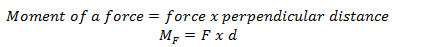
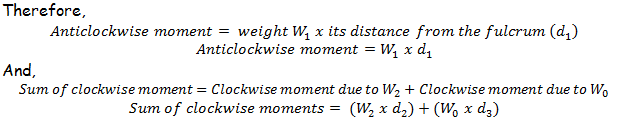
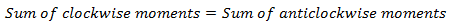
Moment of a Force
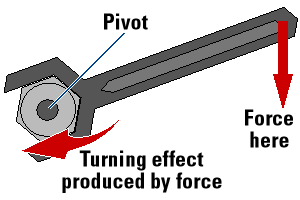
The Effects of Turning Forces
Explain the effects of turning forces
A force is a push or pull which when applied to a body it will change its state either by stopping it if it was in motion or making it move if it was at rest.
If a body under the action of a net externalforceis allowed to rotate about a pivot, the body will tend to turn in the direction of the applied force.

Examples of turning effect of force:
- A person pushing a swing will make the swing rotate about its pivot.
- A worker applies force to a spanner to rotate a nut.
- A person removes a bottle’s cork by pushing down the bottle opener’s lever.
- Force is applied to a door knob and the door swings open about its hinge.
- A driver can turn a steering wheel by applying force on its rim.
The Moment of Force
Determine the moment of force
Moment of force about a point is the turning effect of the force about that point. It is obtained as the product of applied force and the perpendicular distance from the point of the application of the force.
Therefore, moment of a force depends on two factors namely;
- The applied force.
- The perpendicular distance from the point of action of the force to the turning point(fulcrum).
The change of state of a body can appear in several forms and the most common form is the turning effect which is referred to as moment of a force.
The unit for the moment of a force is Newton-meter (Nm).
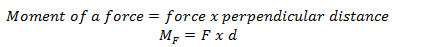
The turning effect can bring about two kinds of moments;
- Clockwise moment -caused by the forces which tend to turn the body in a clockwise direction.
- Anticlockwise moment -caused by the forces which tend to turn the body in an anticlockwise direction.
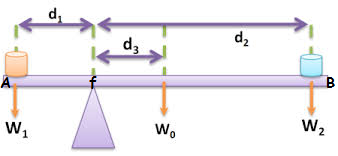
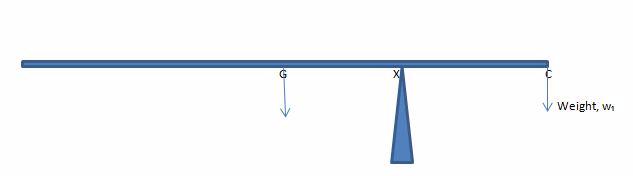
Consider the diagram below,

The above uniform rod AB is balanced about the turning point (fulcrum) f. The weight W1 acting at point A tends to turn the rod in anticlockwise direction. The weight W2 acting at point B and the weight of the rigid body W0 tends to move the rod in clockwise direction. Hence, we have two anticlockwise moments due to weight W2 and weight of the rod W0.
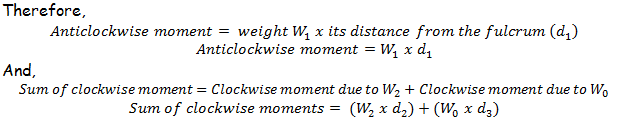
The Principle of Moments
State the principle of moments
The Principle of moments states that:
” If a body is in equilibrium under action of forces which lie on one plane, then, the sum of the clockwise moments is equal to the sum of the anticlockwise moments about any point in that plane.”
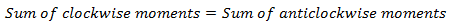
The equilibrium of state of a body is brought about by two conditions;
- The sum of anticlockwise moments is equal to sum of clockwise moments about the turning point.
- The sum of upward forces is equal to sum of downward forces acting on a body.
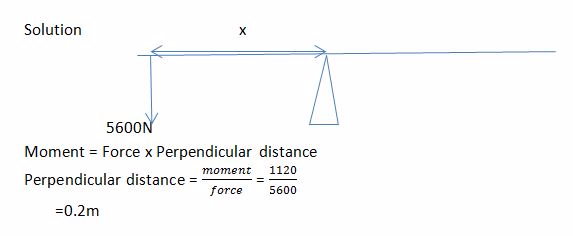
If the data for the weight (force) W, and distance d of the weight from the fulcrum can be obtained then the moment created about the fulcrum is obtained by multiplying the weight with the respective distance i.e Wd. According to the principle of moments, at equilibrium the sum of clockwise moments (Wd) and that of anticlockwise moments (Wd) must be equal. to make it simple the below table can be used to record and compare the moments;
| W1(g) | W2(g) | d1(cm) | d2(cm) | W1d1(gcm) | W2d2(gcm) |
Activity 1
Experiment.
Aim: To determine the moment of a force.
Materials and apparatus:Meter rule, several different weights, inelastic cotton thread, knife edge and a marker pen.
Procedures
- Balance the meter rule horizontally on a knife edge.
- Mark a balance point as C. Use the marker pen to do that.
- Suspend a meter rule from a fixed axis through C. Suspend unequal weights W₁ and W₂ from the meter rule by using thin cotton threads.
- Adjust the distance d₁ and d₂ of the weights W₁ and W₂ from C until the meter rule balance.
- Repeat the experiment five times using different values of W₁ and W₂.Record the results on the table as shown below.
| W₁(g) | W₂(g) | d₁(cm) | d₂(cm) | W₁ d₁ (gcm) | W₂ d₂ (gcm) |
Observation:In each case it will be found that W₁ d₁ is equal to W₂ d₂.
The Principle of Moment in Daily Life
Apply the principle of moment in daily life
Moment of a force is used in the following:
- Is applied by a hand to unscrew a stopper on the bottle.
- Is applied by a spanner to unscrew a nut on a bottle.
- Turning a steering wheel of a car.
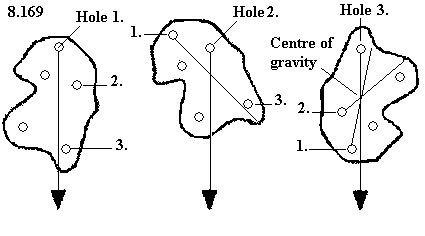
Centre of Gravity
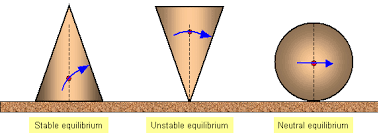
Types of Equilibrium



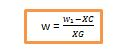

1 Comment
Is good